Defender Game: Dive into the captivating world of games where strategic defense is key! From classic tower defense to innovative base-building challenges, we’ll explore the core mechanics, design elements, and monetization strategies that make these games so engaging. We’ll journey through the evolution of defender game mechanics, examining successful examples and uncovering the secrets behind player retention.
This exploration will cover everything from level design and compelling narratives to the technical aspects of development, including game engines, AI implementation, and optimization across various platforms. We’ll also discuss the importance of balancing difficulty, creating rewarding experiences, and building thriving communities around your defender game.
Defender Game Genres
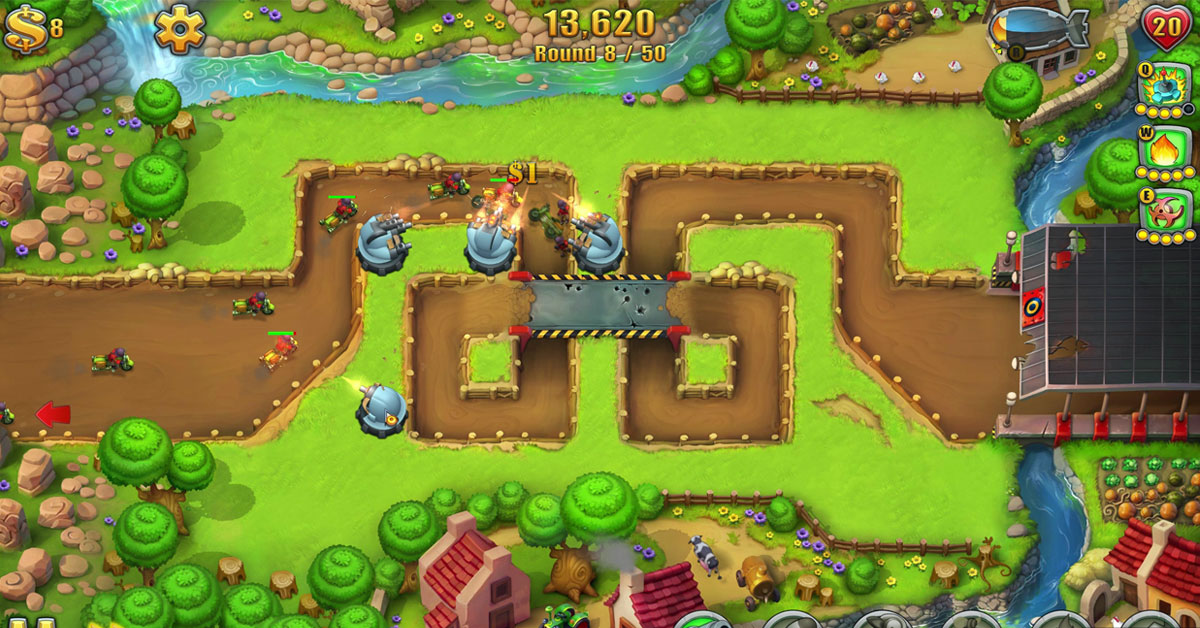
Defender games encompass a broad spectrum of gameplay experiences, all revolving around the core concept of defending a point or area from waves of enemies. This core mechanic is implemented in diverse ways, leading to the emergence of various subgenres.
Core Defender Game Mechanics

The fundamental mechanic of defender games involves strategically deploying defenses to repel incoming threats. This usually includes resource management, unit placement, upgrade systems, and wave-based combat. Success hinges on effective resource allocation, anticipating enemy movements, and adapting to changing challenges.
Defender Game Subgenres
Tower defense (TD) is perhaps the most recognizable subgenre, where players place stationary towers along predefined paths to eliminate advancing enemies. Base defense games expand upon this, often incorporating base-building and resource gathering elements, requiring players to defend a central structure. Other variations exist, such as lane defense, where enemies approach from multiple paths, and real-time strategy (RTS) elements can also be integrated.
Evolution of Defender Game Mechanics
Early defender games often featured simple mechanics and limited unit variety. As technology advanced, so did the complexity of these games. Modern defender games often boast intricate upgrade systems, diverse unit types with unique abilities, and dynamic environments that influence gameplay. The introduction of hero units, special abilities, and environmental hazards has also significantly enriched the experience.
A Novel Defender Game Mechanic: Dynamic Terrain Modification

This mechanic allows players to actively alter the terrain to influence enemy movement and combat effectiveness. For example, players could raise walls, create trenches, or flood areas to slow down or divert enemy advances. This would add a strategic layer beyond simple tower placement, demanding adaptive gameplay.
Game Design Elements in Defender Games
Effective level design, compelling narratives, and strong visual elements are crucial for creating an engaging and memorable defender game experience. The careful balance of these aspects contributes significantly to player satisfaction and retention.
Successful Defender Game Level Design
Good level design in defender games involves creating a gradual increase in difficulty, introducing new enemy types and mechanics at appropriate intervals. Strategic placement of chokepoints, obstacles, and resource nodes can significantly impact the player’s ability to defend. For example, a level might start with a single, easily defended path, gradually branching into multiple paths with varied terrain features and enemy compositions.
Compelling Narratives in Defender Games
While not always a central focus, narratives can add depth and context to defender games. A compelling story can provide a reason for the player’s actions, creating a stronger sense of investment in the game world. Examples include a kingdom under siege, a planet threatened by an alien invasion, or a magical realm facing a demonic incursion.
Visual Elements in Defender Games
Art style, character design, and overall visual presentation are critical in enhancing the player experience. A visually appealing game is more likely to capture and retain players’ attention. The art style should align with the game’s theme and target audience, while character designs should be distinctive and memorable.
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Comparison
A clear and intuitive UI is paramount for a positive UX. Here’s a comparison of three hypothetical defender games:
| Game | UI Clarity | UX Flow | Feedback Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defender Alpha | Excellent; clear icons and intuitive menus. | Smooth and efficient; easy to understand progression. | Real-time updates on resource levels, unit health, etc. |
| Defender Beta | Good; some icons could be more descriptive. | Mostly smooth; some minor navigation issues. | Delayed updates; some lag in visual feedback. |
| Defender Gamma | Fair; cluttered interface; difficult to navigate. | Poor; confusing progression system. | Minimal feedback; unclear what’s happening in-game. |
Monetization Strategies in Defender Games
Free-to-play (F2P) defender games often utilize various monetization methods to generate revenue. It’s crucial to implement these strategies carefully to avoid negatively impacting the gameplay experience.
Common Monetization Methods
- In-app purchases (IAPs): Offering premium currency, cosmetic items, or powerful units for purchase.
- Advertisements: Displaying ads between levels or during gameplay (interstitial or banner ads).
- Subscription models: Offering premium features or content for a recurring fee.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Monetization Strategies
IAPs can generate significant revenue but can be perceived negatively if implemented poorly, leading to pay-to-win scenarios. Advertisements can be intrusive and disruptive, while subscription models may not be appealing to all players.
Impact of In-App Purchases on Gameplay
Poorly implemented IAPs can create an uneven playing field, where paying players have a significant advantage over free players. This can lead to frustration and player churn. Well-designed IAPs, however, offer optional enhancements without compromising the core gameplay experience.
Defender games often involve strategic choices, and sometimes those choices hinge on chance. Think about deciding which upgrade to prioritize – you could use a simple coin toss to settle the matter if you’re stuck. This random element adds a bit of unpredictable fun to the gameplay, making each playthrough feel unique, even in a well-known defender game.
Monetization Model Comparison
Game A might utilize a balanced approach of IAPs for cosmetic items and a subscription model for exclusive content, while Game B might rely heavily on IAPs for powerful units, potentially creating a pay-to-win environment.
Defender games often test your strategic skills, making you think carefully about resource management and unit placement. If you enjoy that kind of pressure-cooker gameplay, you might also like the intense choices in until dawn game , where your decisions directly impact the story. Then, after experiencing that narrative-driven tension, you can jump back into the more tactical challenge of a good defender game and put your improved decision-making to the test.
Player Engagement and Retention in Defender Games
Maintaining player engagement and retention is vital for the long-term success of any defender game. This requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing various strategies to keep players invested and returning.
Methods for Improving Player Engagement and Retention

- Regular content updates: Introducing new levels, units, challenges, and features to maintain freshness.
- Reward systems: Implementing systems that reward consistent play, achievement milestones, and participation in community events.
- Community building: Fostering a sense of community through forums, social media, and in-game interactions.
Successful Reward Systems
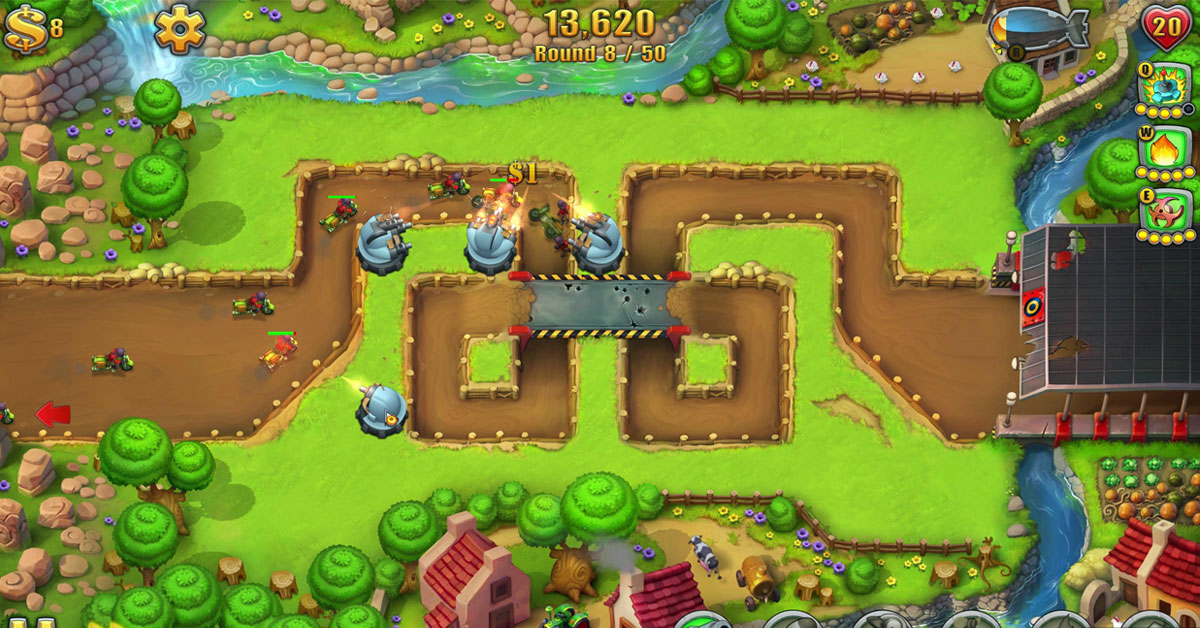
Examples include daily login bonuses, achievement rewards, seasonal events with exclusive rewards, and leaderboards to encourage competition.
Role of Community Building
A strong community can provide players with a sense of belonging, encourage collaboration, and generate valuable feedback for developers.
Defender games often involve strategic choices, and sometimes those choices feel a bit like a gamble. Think about it – a key decision might hinge on whether you risk everything to attack or defend, much like deciding heads or tails in a coin toss game. Ultimately, in both cases, smart planning and a bit of luck determine your success in the defender game.
Regular Update Schedule
A consistent update schedule with planned content releases helps maintain player interest and anticipation. This schedule should be communicated clearly to the player base.
Technical Aspects of Defender Games
The technical aspects of defender game development encompass various elements, from choosing the right game engine to optimizing performance across different platforms.
Common Game Engines
Popular game engines used for developing defender games include Unity, Unreal Engine, and GameMaker Studio 2. The choice of engine depends on factors such as budget, team expertise, and target platform.
Optimization for Different Platforms
Optimizing for different platforms (mobile, PC, etc.) requires careful consideration of hardware limitations and performance requirements. Mobile games often require more aggressive optimization to ensure smooth gameplay on a wider range of devices.
Balancing Difficulty and Progression, Defender game
A well-balanced game provides a challenging yet rewarding experience. Difficulty should scale gradually, introducing new mechanics and enemies at an appropriate pace, preventing frustration and maintaining player engagement.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Enemy Behavior
AI plays a crucial role in creating engaging enemy behavior. Sophisticated AI can lead to unpredictable enemy movements, strategic attacks, and adaptive behavior, enhancing the challenge and replayability of the game.
Illustrative Examples of Defender Games
The following are descriptions of three hypothetical defender games, highlighting their unique aspects.
- Game A: A vibrant, cartoonish tower defense game set in a whimsical fantasy world. Players defend adorable animal villages from waves of mischievous goblins using quirky towers with unique abilities. Strengths include charming visuals and accessible gameplay; weaknesses might include a lack of depth in later levels.
- Game B: A gritty, realistic base defense game set in a post-apocalyptic wasteland. Players must scavenge resources, build defenses, and manage dwindling supplies while fending off hordes of mutated creatures. Strengths lie in its atmospheric setting and challenging gameplay; weaknesses could include a steep learning curve.
- Game C: A stylized, futuristic tower defense game with a strong emphasis on strategic unit placement and upgrades. Players defend a technologically advanced city from waves of robotic invaders using a variety of high-tech weaponry. Strengths include complex mechanics and strategic depth; weaknesses might include a less accessible learning curve for casual players.
Outcome Summary
Creating a successful defender game requires a blend of strategic gameplay, engaging narratives, and smart monetization. By understanding the core mechanics, optimizing the user experience, and fostering a strong community, developers can craft truly captivating experiences that keep players coming back for more. Remember, the key is to find the right balance between challenge and reward, creating a game that’s both fun and rewarding.
Essential FAQs
What are some examples of successful defender game reward systems?
Successful reward systems often include daily login bonuses, achievement rewards, tiered progression systems, and loot boxes (used cautiously and transparently).
How important is AI in defender games?
AI is crucial for creating challenging and engaging enemy behavior. It dictates enemy pathfinding, attack patterns, and strategic decision-making, significantly impacting the gameplay experience.
What are the common challenges in optimizing defender games for mobile?
Mobile optimization often focuses on balancing performance with visual fidelity, considering battery life, and adapting controls for touchscreens. Balancing game size for downloads is also key.
What are some less common defender game subgenres?
Beyond tower and base defense, consider resource management defenders, wave-based survival defenders, and even RPG-infused defender games.